[ad_1]
Opinion from Dr. Andreas Freund. 21 August 2024
TL/DR
There are platform options for DeFi protocols to combine regulatory compliance with out compromising decentralization. Utilizing blockchain expertise and cryptographic protocols, DeFi protocols can guarantee safe and clear transactions that meet regulatory requirements whereas sustaining consumer privateness. Such protocols implement compliance guidelines on digital property and their holders. Due to this fact, they’ll present a sturdy and versatile system to assist DeFi protocols navigate the advanced regulatory panorama, contributing to a safer and extra dependable decentralized monetary ecosystem.
Introduction
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has taken the monetary world by storm (no less than within the OpEd pages of Bloomberg and Fortune), providing a permissionless and clear different to conventional monetary establishments with a complete locked worth (TVL), as of this writing, of practically $100Bn. Nevertheless, this very decentralization creates a significant hurdle: compliance. In contrast to typical establishments with central management, DeFi protocols are sometimes ruled by self-executing code and lack a single entity liable for imposing laws. This raises a crucial query: how can these revolutionary protocols combine compliance guidelines into their DNA with out compromising their core rules of decentralization and autonomy? This problem lies on the coronary heart of DeFi’s future, as regulators grapple with discovering the suitable steadiness between fostering innovation and defending shoppers since practically all of the ~ $100Bn in TVL and billions of {dollars} every day trades on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) based on DeFi Lama haven’t undergone any correct compliance checks. Sadly, and really just lately, regulators have resorted to authorized motion towards the likes of Uniswap, Twister Money, and different DeFi protocols.
After thumbing their noses at regulators for a few years, the organizations constructing DeFi protocols at the moment are realizing two issues:
- The phrases decentralization and No-Management don’t shield towards costly authorized actions.
- DeFi mass adoption requires higher UX and compliance enforcement — each monetary and information privateness, and on the similar time.
Even when DeFi protocols wished to implement compliance checks instantly, it will not solely upset their greatest consumer’s apple carts however would require protocol rewrites. In different phrases, fully new variations of the protocol with older variations nonetheless working with none compliance checks. That’s not a tenable scenario, since, very doubtless, the foundations or DAOs governing DeFi protocols would nonetheless be held to account for non-compliant variations of their protocol since “good contracts are endlessly” — sure, Marilyn Monroe pun quote meant.
Fortunately there’s a method ahead for these protocols. Leveraging blockchain-native compliance mechanisms – a mixture of good contracts, and blockchain-verifiable zero-knowledge proofs, representing assertions {that a} consumer and submitted asset transaction are compliant with the relevant legislation in a jurisdiction, yields a complete framework to make sure regulatory compliance, threat administration, and transaction reporting for any digital asset. The instructed framework extends the work initially performed by Azgad-Tromer et. al (2023) that mixes strong regulatory compliance actions with privateness safety, enabling, for instance, the creation of compliant variations of digital property that implement jurisdictional insurance policies whereas being privacy-preserving. The unique framework by Azgad-Tromer et al. preserves digital property’ financial worth and technological capabilities whereas guaranteeing that delicate info is selectively seen solely to approved legislation enforcement authorities – Fincen, SEC, OFAC, and many others. This enhances the safety and integrity of digital asset transactions whereas sustaining privateness for respectable customers. Furthermore, the framework’s compatibility with several types of digital property equivalent to fungible and non-fungible digital property makes it a flexible answer.
Briefly, the framework augments blockchains with further details about actors’ identities and asset provenance in a privacy-preserving method and was first applied by Sealance. This revolutionary method allows the framework to handle the challenges posed by the decentralized nature of digital property. Attaching Compliance-Related Auxiliary Data (CRAI) to transactions involving digital property in encrypted type ensures that crucial compliance information, equivalent to consumer identities, credentials, transaction historical past, and fund provenance, stays safe and tamper-proof – see FinCen steering on Anit-Cash-Laundering for example. The framework incorporates cryptographic protocols that may routinely implement compliance insurance policies assigned to digital property — what holders can and can’t do with such a digital asset — and digital asset holders — what property people can and can’t maintain and/or commerce. It could possibly additionally replace CRAI through the recording of transactions on the blockchain. This integration permits real-time compliance monitoring and reporting, enhancing transparency and accountability within the digital asset ecosystem.
Notice, that earlier work on this space was performed by Kaira et al. in 2021 for the case of a centrally managed Hedge Fund. Whereas complementary to this dialogue, it doesn’t contact on KYC/AML compliance, which is the central query we’re discussing on this paper.
The right way to make DeFi Protocols Regulatory Compliant
So how does such a framework function within the context of DeFi protocols, given that almost all property on these platforms usually are not natively regulatory compliant?
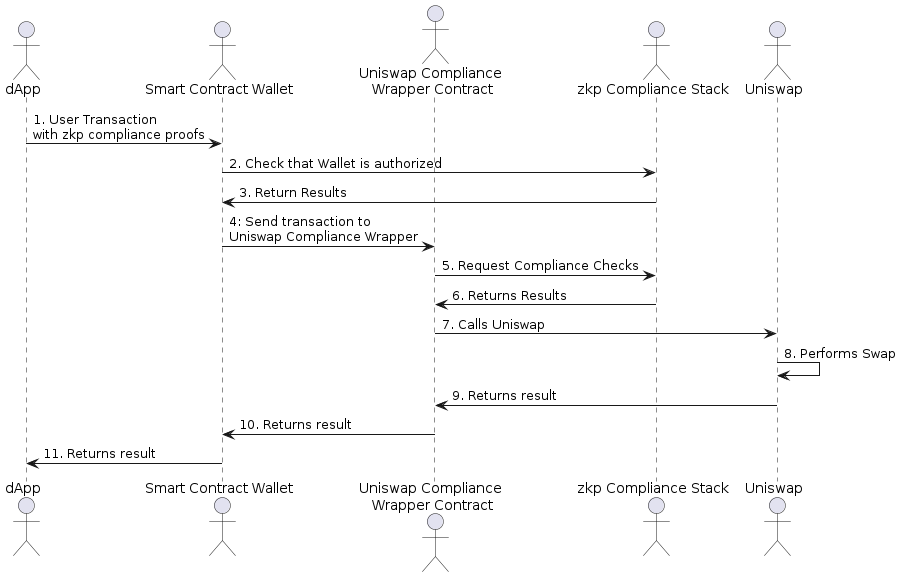
Fig. 1: Excessive-Degree DeFi (ZKP) Compliance Structure as an extension of Azgad-Tromer et al.
The important thing perception within the extension of the Azgad-Tromer et al. framework is {that a} good contract pockets used, for instance, in Account Abstraction (see EIP-4337) as a consultant of a number of Entity Owned Accounts (EOA) has considerably extra flexibility as a result of its programmability than an EOA. If a wise contract pockets is mixed with different good contracts that implement compliance guidelines and work together with a DeFi protocol we’ve got all of the substances we want. Consider a wise contract pockets as functionally equal to a standard Dealer-Vendor, a regulated and registered entity, that locations trades for his or her shoppers, and a DeFi protocol with a number of compliance imposing good contracts as a registered inventory or commodity change with its buying and selling and compliance capabilities. Notice {that a} Dealer-Vendor is a *registered entity* that may be a *authorized delegate* of an everyday investor to position trades on the investor’s behalf and implement commerce compliance guidelines. The inventory change is one other *registered entity* – registered with regulatory authorities such because the SEC or Fincen – and its compliance and buying and selling capabilities are separate by design — separation of issues is a major compliance rule.
With this analogy in thoughts, we are able to now assemble a regulatory-compliant DeFi protocol stack built-in with a compliance framework such because the one pioneered by Sealance by coverage supervisor contracts with related compliance insurance policies, and a compliance coverage and compliant account registry. Probably the most simple implementation is thru “good contract hooks” in DeFi protocols as they permit customized compliance enforcement extensions to the protocol, for instance, Uniswap V4 or Seaport. Nevertheless, this doesn’t clear up the problem for DeFi protocols that should not have such capabilities; at the moment nonetheless the bulk.
There’s a normal secure sample to work together with DeFi protocols that should not have contract hooks for compliance checks when a consumer receives a yield-bearing instrument such because the Compound yield token (YT) e.g. cDai. In our description beneath, we implicitly assume that DeFi protocol contracts such because the Uniswap Router or Place Supervisor are registered contracts such that the compliance coverage enforcement mechanism embedded in “compliant” property can establish them as compliant and never require an extra zkp compliance assertion to be embedded with, for instance, a switch perform.
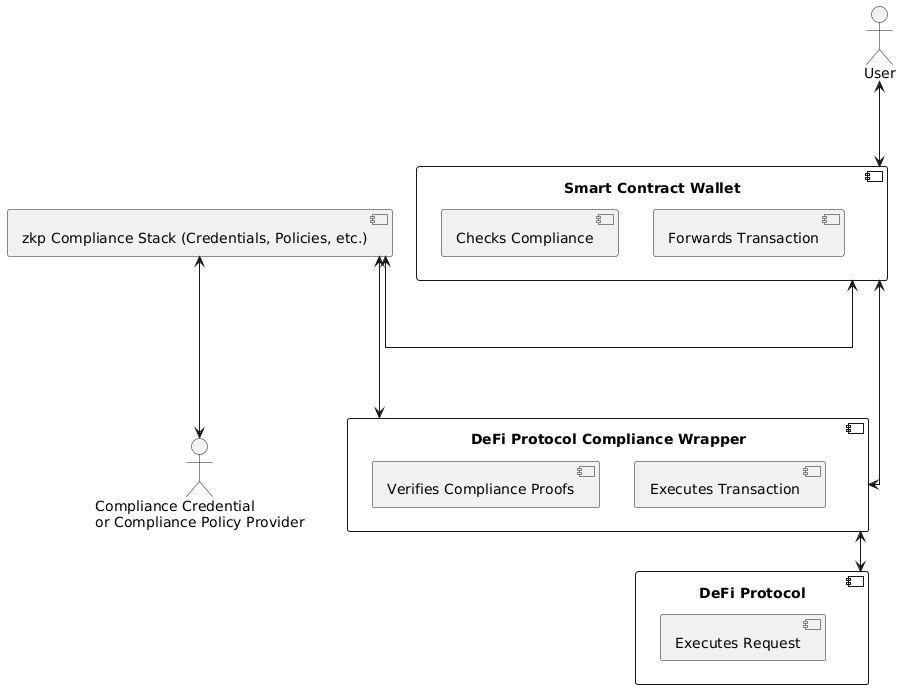
Fig. 2: Instance zkp-Compliance Stack utility with Unsiwap and compliant good contract pockets
A compliance-safe DeFi interplay sample is described beneath utilizing the instance of including liquidity to a Uniswap Liquidity Pool for specificity:
- A consumer (EOA) calls a DeFi Protocol compliance (wrapper, also called a logical abstraction) contract immediately or by the consumer’s Good Contract Pockets in an account abstraction state of affairs.
Notice: the good contract pockets has already been given a Energy-Of-Lawyer certificates by an accepted KYC/AML supplier, equivalent to a financial institution or an change. This certificates is utilized in the identical method as a real-world Energy-Of-Lawyer works; it marks the good contract pockets as ready to make use of the zero-knowledge proof (zkp) assertions of compliance that the zk-based compliance platform creates for a consumer’s asset transactions. - The DeFi (wrapper) contract verifies the submitted zkp compliance assertions utilizing the zk-based compliance stack – a wise contract system see Fig 1 – routing compliance assertions within the type of zk-proofs to (compliance) coverage enforcement factors (PEP) – good contracts as a part of the zk compliance stack) the place proofs are verified and actions aka transactions are both allowed or denied. If the compliance checks are profitable, liquidity is added to a pool — both a pool of compliant or uncompliant property — on behalf of the consumer by the DeFi (wrapper) contract. Let’s assume for the next a compliant asset pool
- The DeFi compliance (wrapper) contract receives the YT and creates a compliant YT asset using one of many zkp assertions supplied by the consumer.
- The DeFi compliance (wrapper) contract then transfers the now compliant YT to the EOA or the good contract pockets — this additionally requires a zkp compliance assertion.
This prevents customers from buying and selling non-compliant YTs except the consumer manually unwraps the asset. Notice that every one the yield now accumulates to the compliant YT. A variant of this method is utilizing DeFi compliance library contracts with the identical performance as a compliance wrapper contract whereas not requiring belief within the preliminary wrapper contract deployment.
For DeFi protocol transactions of compliant property (e.g. lending, swaps) or compliant property with non–compliant property (e.g. swaps), there’s an extra sample:
- A Consumer (EOA) can make the most of an authority delegation coverage expressed as a PEP for its good contract pockets such that the good contract pockets can work together with a compliant asset with out being required to provide a zkp compliance assertion. This may be achieved by the consumer making a delegating zkp compliance assertion (delegation to good contract pockets) and submitting it to the zk-based compliance stack to be validated after which registered with a particular Energy-Of-Lawyer coverage inside a PEP. Energy-of-attorney-type insurance policies can exist at a jurisdictional degree, by asset class, and even on the degree of particular person property.
Key Level: An authority delegation coverage to be utilized in a transaction is on the asset degree, not the extent of a payee, a payer, or an authorizer degree. This permits an asset to establish if a payer or payee is permitted to work together with it, with out being required to provide a zkp compliance assertion. - Identified DeFi protocol good contracts e.g. Uniswap Router, or an Aave Lending Pool supervisor can, due to this fact, additionally make the most of a Proof Delegation coverage as described above. The first distinction is that on this context the entity creating the delegation zkp compliance assertion (regulatory whitelisting of a Defi protocol good contract), and the registration is completed by a certified coverage creator or registrar equivalent to a KYC supplier throughout the zk-based compliance ecosystem.
Key Level: As within the case of an EOA, this registrar-proof-delegation coverage is on the degree of the asset, and might differentiate jurisdiction, asset class, and even particular person asset. Nevertheless, it’s of a distinct authority delegation coverage sort as a result of the requester has one other ecosystem function. Due to this fact, the compliant asset will need to have each sorts of authorization delegation insurance policies connected to it as a result of each a wise contract pockets, a Defi protocol compliance wrapper, and a Defi Protocol good contract will work together with the compliant asset.
Conclusion
In abstract, to make sure the longevity and acceptance of DeFi protocols by mainstream customers, these protocols should transfer in the direction of regulatory compliance. The described compliance platform, an extension of the framework proposed by Azgad-Tromer et al. and applied by Sealance, provides a sensible answer permitting DeFi protocols to include compliance measures whereas sustaining decentralization. It makes use of blockchain expertise and superior cryptographic protocols for clear, safe transactions that meet regulatory necessities, all whereas preserving consumer privateness. It enforces compliance guidelines on digital property and their homeowners, offering a stable and versatile system. The important thing advantages of the described compliance framework for DeFi protocols are:
- Regulatory Compliance: The framework allows DeFi protocols to stick to regulatory requirements with out compromising their decentralized nature (although KYC is essentially nonetheless performed by centralized entities).
- Danger Administration: The framework allows mechanisms for efficient threat administration and transaction reporting for numerous digital property.
- Privateness Safety: The framework incorporates cryptographic privacy-preserving options equivalent to zkps guaranteeing that delicate consumer info utilized in compliance credentials and in creating zkp compliance coverage assertions stays confidential, with private info saved and accessible solely by KYC/AML or different compliance credential suppliers equivalent to banks or exchanges
- Safety: Leveraging secure cryptographic protocols, the framework can improve the safety and integrity of digital asset transactions by imposing advanced enterprise guidelines.
- Versatility: It’s suitable with several types of digital property, together with fungible and non-fungible tokens, making it a flexible answer for the DeFi ecosystem.
- Transparency and Accountability: The framework promotes transparency and accountability within the DeFi area by real-time compliance monitoring and reporting (by onchain submitted, totally encrypted studies).
Such a framework can help DeFi protocols in navigating the intricate regulatory setting, contributing to a safer and extra reliable decentralized monetary ecosystem.
Dr Freund might be contacted through e-mail at [email protected]
[ad_2]
